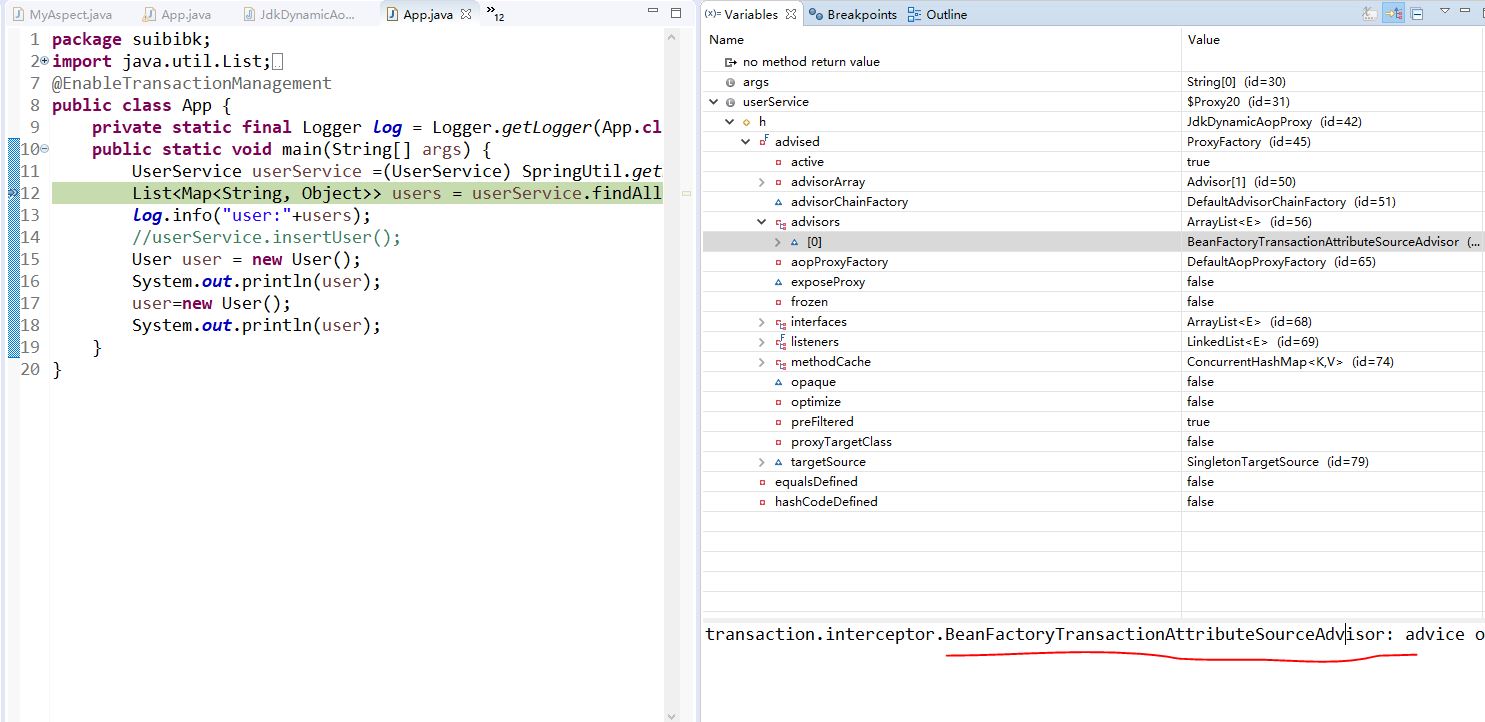
通过上一篇文章一个简单的例子来探寻SpringAOP执行源码的主脉络(二):执行代理方法 我们知道了AOP怎么执行代理方法,主要是靠对应的Advisor,我们知道spring会为我们的切面里面的方法比befor,after,around等方法都生成对应的Advisor,所以我们估计spring事务的代理方法逻辑跟AOP是差不多的,主要看的就是对应的Advisor里面的执行逻辑,在一个简单的例子来探寻Spring事务Trasanction执行源码的主脉络(一):创建事务代理对象文章中,我们已经知道了事务对应的Advisor是BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor,那应该是跑不了了。
我们来调试下看看
果然不出预料,那么前面的逻辑肯定是跟AOP差不多的。
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {Object oldProxy = null;boolean setProxyContext = false;TargetSource targetSource = this.advised.targetSource;Object target = null;try {if (!this.equalsDefined && AopUtils.isEqualsMethod(method)) {// The target does not implement the equals(Object) method itself.return equals(args[0]);}else if (!this.hashCodeDefined && AopUtils.isHashCodeMethod(method)) {// The target does not implement the hashCode() method itself.return hashCode();}else if (method.getDeclaringClass() == DecoratingProxy.class) {// There is only getDecoratedClass() declared -> dispatch to proxy config.return AopProxyUtils.ultimateTargetClass(this.advised);}else if (!this.advised.opaque && method.getDeclaringClass().isInterface() &&method.getDeclaringClass().isAssignableFrom(Advised.class)) {// Service invocations on ProxyConfig with the proxy config...return AopUtils.invokeJoinpointUsingReflection(this.advised, method, args);}Object retVal;if (this.advised.exposeProxy) {// Make invocation available if necessary.oldProxy = AopContext.setCurrentProxy(proxy);setProxyContext = true;}// Get as late as possible to minimize the time we "own" the target,// in case it comes from a pool.target = targetSource.getTarget();Class<?> targetClass = (target != null ? target.getClass() : null);// Get the interception chain for this method.List<Object> chain = this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method, targetClass);// Check whether we have any advice. If we don't, we can fallback on direct// reflective invocation of the target, and avoid creating a MethodInvocation.if (chain.isEmpty()) {// We can skip creating a MethodInvocation: just invoke the target directly// Note that the final invoker must be an InvokerInterceptor so we know it does// nothing but a reflective operation on the target, and no hot swapping or fancy proxying.Object[] argsToUse = AopProxyUtils.adaptArgumentsIfNecessary(method, args);retVal = AopUtils.invokeJoinpointUsingReflection(target, method, argsToUse);}else {// We need to create a method invocation...MethodInvocation invocation =new ReflectiveMethodInvocation(proxy, target, method, args, targetClass, chain);// Proceed to the joinpoint through the interceptor chain.retVal = invocation.proceed();}// Massage return value if necessary.Class<?> returnType = method.getReturnType();if (retVal != null && retVal == target &&returnType != Object.class && returnType.isInstance(proxy) &&!RawTargetAccess.class.isAssignableFrom(method.getDeclaringClass())) {// Special case: it returned "this" and the return type of the method// is type-compatible. Note that we can't help if the target sets// a reference to itself in another returned object.retVal = proxy;}else if (retVal == null && returnType != Void.TYPE && returnType.isPrimitive()) {throw new AopInvocationException("Null return value from advice does not match primitive return type for: " + method);}return retVal;}finally {if (target != null && !targetSource.isStatic()) {// Must have come from TargetSource.targetSource.releaseTarget(target);}if (setProxyContext) {// Restore old proxy.AopContext.setCurrentProxy(oldProxy);}}}
不过在这里我们发现
List<Object> chain = this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method, targetClass);
这里生成的调用链里面的对象是TransactionInterceptor这个是该advisor里面的advice(通知)的invoke方法,在生成代理对象的步骤中也会把这个bean加入到容器中的。前面的调用模式跟AOP一个样,接下来我们直接进入到这个对象的invoke方法
@Override@Nullablepublic Object invoke(MethodInvocation invocation) throws Throwable {// Work out the target class: may be {@code null}.// The TransactionAttributeSource should be passed the target class// as well as the method, which may be from an interface.Class<?> targetClass = (invocation.getThis() != null ? AopUtils.getTargetClass(invocation.getThis()) : null);// Adapt to TransactionAspectSupport's invokeWithinTransaction...return invokeWithinTransaction(invocation.getMethod(), targetClass, invocation::proceed);}
我们直接进入到
return invokeWithinTransaction(invocation.getMethod(), targetClass, invocation::proceed);
方法中,真相应该就在这里
@Nullableprotected Object invokeWithinTransaction(Method method, @Nullable Class<?> targetClass,final InvocationCallback invocation) throws Throwable {// If the transaction attribute is null, the method is non-transactional.//这个是我们的那个advisorTransactionAttributeSource tas = getTransactionAttributeSource();final TransactionAttribute txAttr = (tas != null ? tas.getTransactionAttribute(method, targetClass) : null);//这个是我们之前指定的:DataSourceTransactionManagerfinal TransactionManager tm = determineTransactionManager(txAttr);if (this.reactiveAdapterRegistry != null && tm instanceof ReactiveTransactionManager) {ReactiveTransactionSupport txSupport = this.transactionSupportCache.computeIfAbsent(method, key -> {if (KotlinDetector.isKotlinType(method.getDeclaringClass()) && KotlinDelegate.isSuspend(method)) {throw new TransactionUsageException("Unsupported annotated transaction on suspending function detected: " + method +". Use TransactionalOperator.transactional extensions instead.");}ReactiveAdapter adapter = this.reactiveAdapterRegistry.getAdapter(method.getReturnType());if (adapter == null) {throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot apply reactive transaction to non-reactive return type: " +method.getReturnType());}return new ReactiveTransactionSupport(adapter);});return txSupport.invokeWithinTransaction(method, targetClass, invocation, txAttr, (ReactiveTransactionManager) tm);}PlatformTransactionManager ptm = asPlatformTransactionManager(tm);final String joinpointIdentification = methodIdentification(method, targetClass, txAttr);if (txAttr == null || !(ptm instanceof CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager)) {// Standard transaction demarcation with getTransaction and commit/rollback calls.//这里是创建事务,如果需要的话,也就是如果你在被代理的方法那里加了@Transation注解的话,这里就会创建一个事务TransactionInfo txInfo = createTransactionIfNecessary(ptm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification);Object retVal;try {// This is an around advice: Invoke the next interceptor in the chain.// This will normally result in a target object being invoked.retVal = invocation.proceedWithInvocation();}catch (Throwable ex) {// target invocation exceptioncompleteTransactionAfterThrowing(txInfo, ex);throw ex;}finally {cleanupTransactionInfo(txInfo);}if (retVal != null && vavrPresent && VavrDelegate.isVavrTry(retVal)) {// Set rollback-only in case of Vavr failure matching our rollback rules...TransactionStatus status = txInfo.getTransactionStatus();if (status != null && txAttr != null) {retVal = VavrDelegate.evaluateTryFailure(retVal, txAttr, status);}}commitTransactionAfterReturning(txInfo);return retVal;}else {Object result;final ThrowableHolder throwableHolder = new ThrowableHolder();// It's a CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager: pass a TransactionCallback in.try {result = ((CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager) ptm).execute(txAttr, status -> {TransactionInfo txInfo = prepareTransactionInfo(ptm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification, status);try {Object retVal = invocation.proceedWithInvocation();if (retVal != null && vavrPresent && VavrDelegate.isVavrTry(retVal)) {// Set rollback-only in case of Vavr failure matching our rollback rules...retVal = VavrDelegate.evaluateTryFailure(retVal, txAttr, status);}return retVal;}catch (Throwable ex) {if (txAttr.rollbackOn(ex)) {// A RuntimeException: will lead to a rollback.if (ex instanceof RuntimeException) {throw (RuntimeException) ex;}else {throw new ThrowableHolderException(ex);}}else {// A normal return value: will lead to a commit.throwableHolder.throwable = ex;return null;}}finally {cleanupTransactionInfo(txInfo);}});}catch (ThrowableHolderException ex) {throw ex.getCause();}catch (TransactionSystemException ex2) {if (throwableHolder.throwable != null) {logger.error("Application exception overridden by commit exception", throwableHolder.throwable);ex2.initApplicationException(throwableHolder.throwable);}throw ex2;}catch (Throwable ex2) {if (throwableHolder.throwable != null) {logger.error("Application exception overridden by commit exception", throwableHolder.throwable);}throw ex2;}// Check result state: It might indicate a Throwable to rethrow.if (throwableHolder.throwable != null) {throw throwableHolder.throwable;}return result;}}
我们先去看看创建事务的逻辑
@SuppressWarnings("serial")protected TransactionInfo createTransactionIfNecessary(@Nullable PlatformTransactionManager tm,@Nullable TransactionAttribute txAttr, final String joinpointIdentification) {// If no name specified, apply method identification as transaction name.if (txAttr != null && txAttr.getName() == null) {txAttr = new DelegatingTransactionAttribute(txAttr) {@Overridepublic String getName() {return joinpointIdentification;}};}TransactionStatus status = null;if (txAttr != null) {if (tm != null) {status = tm.getTransaction(txAttr);}else {if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {logger.debug("Skipping transactional joinpoint [" + joinpointIdentification +"] because no transaction manager has been configured");}}}return prepareTransactionInfo(tm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification, status);}
继续进入tm.getTransaction(txAttr);
@Overridepublic final TransactionStatus getTransaction(@Nullable TransactionDefinition definition)throws TransactionException {// Use defaults if no transaction definition given.//这里默认的是PROPAGATION_REQUIRED,ISOLATION_DEFAULTTransactionDefinition def = (definition != null ? definition : TransactionDefinition.withDefaults());Object transaction = doGetTransaction();boolean debugEnabled = logger.isDebugEnabled();if (isExistingTransaction(transaction)) {// Existing transaction found -> check propagation behavior to find out how to behave.return handleExistingTransaction(def, transaction, debugEnabled);}// Check definition settings for new transaction.if (def.getTimeout() < TransactionDefinition.TIMEOUT_DEFAULT) {throw new InvalidTimeoutException("Invalid transaction timeout", def.getTimeout());}// No existing transaction found -> check propagation behavior to find out how to proceed.if (def.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_MANDATORY) {throw new IllegalTransactionStateException("No existing transaction found for transaction marked with propagation 'mandatory'");}else if (def.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_REQUIRED ||def.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW ||def.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_NESTED) {SuspendedResourcesHolder suspendedResources = suspend(null);if (debugEnabled) {logger.debug("Creating new transaction with name [" + def.getName() + "]: " + def);}try {//这里会开启一个事务return startTransaction(def, transaction, debugEnabled, suspendedResources);}catch (RuntimeException | Error ex) {resume(null, suspendedResources);throw ex;}}else {// Create "empty" transaction: no actual transaction, but potentially synchronization.if (def.getIsolationLevel() != TransactionDefinition.ISOLATION_DEFAULT && logger.isWarnEnabled()) {logger.warn("Custom isolation level specified but no actual transaction initiated; " +"isolation level will effectively be ignored: " + def);}boolean newSynchronization = (getTransactionSynchronization() == SYNCHRONIZATION_ALWAYS);return prepareTransactionStatus(def, null, true, newSynchronization, debugEnabled, null);}}
我们具体看看怎么开启事务
/*** Start a new transaction.*/private TransactionStatus startTransaction(TransactionDefinition definition, Object transaction,boolean debugEnabled, @Nullable SuspendedResourcesHolder suspendedResources) {boolean newSynchronization = (getTransactionSynchronization() != SYNCHRONIZATION_NEVER);DefaultTransactionStatus status = newTransactionStatus(definition, transaction, true, newSynchronization, debugEnabled, suspendedResources);doBegin(transaction, definition);prepareSynchronization(status, definition);return status;}
当然是doBegin方法啦
@Overrideprotected void doBegin(Object transaction, TransactionDefinition definition) {DataSourceTransactionObject txObject = (DataSourceTransactionObject) transaction;Connection con = null;try {if (!txObject.hasConnectionHolder() ||txObject.getConnectionHolder().isSynchronizedWithTransaction()) {Connection newCon = obtainDataSource().getConnection();if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {logger.debug("Acquired Connection [" + newCon + "] for JDBC transaction");}txObject.setConnectionHolder(new ConnectionHolder(newCon), true);}txObject.getConnectionHolder().setSynchronizedWithTransaction(true);//这里获取一个数据库连接con = txObject.getConnectionHolder().getConnection();Integer previousIsolationLevel = DataSourceUtils.prepareConnectionForTransaction(con, definition);txObject.setPreviousIsolationLevel(previousIsolationLevel);txObject.setReadOnly(definition.isReadOnly());// Switch to manual commit if necessary. This is very expensive in some JDBC drivers,// so we don't want to do it unnecessarily (for example if we've explicitly// configured the connection pool to set it already).if (con.getAutoCommit()) {txObject.setMustRestoreAutoCommit(true);if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {logger.debug("Switching JDBC Connection [" + con + "] to manual commit");}//关闭自动提交:这里就开启了事务,事务的提交由我们自己控制con.setAutoCommit(false);}prepareTransactionalConnection(con, definition);txObject.getConnectionHolder().setTransactionActive(true);int timeout = determineTimeout(definition);if (timeout != TransactionDefinition.TIMEOUT_DEFAULT) {txObject.getConnectionHolder().setTimeoutInSeconds(timeout);}// Bind the connection holder to the thread.if (txObject.isNewConnectionHolder()) {TransactionSynchronizationManager.bindResource(obtainDataSource(), txObject.getConnectionHolder());}}catch (Throwable ex) {if (txObject.isNewConnectionHolder()) {DataSourceUtils.releaseConnection(con, obtainDataSource());txObject.setConnectionHolder(null, false);}throw new CannotCreateTransactionException("Could not open JDBC Connection for transaction", ex);}}
找到了我们的关键性代码
con.setAutoCommit(false);
关闭了自动提交。好了这里如果需要事务的话就开启,我们这里开启了再回到我们之前的代码
if (txAttr == null || !(ptm instanceof CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager)) {// Standard transaction demarcation with getTransaction and commit/rollback calls.TransactionInfo txInfo = createTransactionIfNecessary(ptm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification);Object retVal;try {// This is an around advice: Invoke the next interceptor in the chain.// This will normally result in a target object being invoked.//这里会先去执行我们的业务逻辑方法retVal = invocation.proceedWithInvocation();}catch (Throwable ex) {//如果有异常,则会到这里去回滚// target invocation exceptioncompleteTransactionAfterThrowing(txInfo, ex);throw ex;}finally {cleanupTransactionInfo(txInfo);}if (retVal != null && vavrPresent && VavrDelegate.isVavrTry(retVal)) {// Set rollback-only in case of Vavr failure matching our rollback rules...TransactionStatus status = txInfo.getTransactionStatus();if (status != null && txAttr != null) {retVal = VavrDelegate.evaluateTryFailure(retVal, txAttr, status);}}commitTransactionAfterReturning(txInfo);return retVal;}
开启事务后,这里会先执行业务逻辑方法
retVal = invocation.proceedWithInvocation();
这行代码会回到我们再AOP里面熟悉的
if (this.currentInterceptorIndex == this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.size() - 1) {return invokeJoinpoint();}
而 invokeJoinpoint()会执行具体的业务逻辑。
如果有抛出异常,这里会被catch方法捕获到
我们看下回滚的逻辑
protected void completeTransactionAfterThrowing(@Nullable TransactionInfo txInfo, Throwable ex) {if (txInfo != null && txInfo.getTransactionStatus() != null) {if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {logger.trace("Completing transaction for [" + txInfo.getJoinpointIdentification() +"] after exception: " + ex);}//这里需要检查是否需要回滚if (txInfo.transactionAttribute != null && txInfo.transactionAttribute.rollbackOn(ex)) {try {txInfo.getTransactionManager().rollback(txInfo.getTransactionStatus());}catch (TransactionSystemException ex2) {logger.error("Application exception overridden by rollback exception", ex);ex2.initApplicationException(ex);throw ex2;}catch (RuntimeException | Error ex2) {logger.error("Application exception overridden by rollback exception", ex);throw ex2;}}else {// We don't roll back on this exception.// Will still roll back if TransactionStatus.isRollbackOnly() is true.try {//如果不是运行期异常,我们还是会回滚的txInfo.getTransactionManager().commit(txInfo.getTransactionStatus());}catch (TransactionSystemException ex2) {logger.error("Application exception overridden by commit exception", ex);ex2.initApplicationException(ex);throw ex2;}catch (RuntimeException | Error ex2) {logger.error("Application exception overridden by commit exception", ex);throw ex2;}}}}
我们先判断了一下这个异常是否是
@Overridepublic boolean rollbackOn(Throwable ex) {return (ex instanceof RuntimeException || ex instanceof Error);}
RuntimeException,如果是运行期异常,如果是才会回滚,否则就直接提交。
如果没有抛出异常就会执行到
commitTransactionAfterReturning(txInfo);
很明显就是提交事务啦
/*** Execute after successful completion of call, but not after an exception was handled.* Do nothing if we didn't create a transaction.* @param txInfo information about the current transaction*/protected void commitTransactionAfterReturning(@Nullable TransactionInfo txInfo) {if (txInfo != null && txInfo.getTransactionStatus() != null) {if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {logger.trace("Completing transaction for [" + txInfo.getJoinpointIdentification() + "]");}txInfo.getTransactionManager().commit(txInfo.getTransactionStatus());}}
好了!其实总结一句,看AOP还是事务,还是别的什么组件,主要是看Advisor里面的advice。