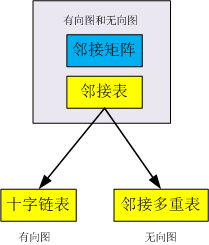
图的存储结构优缺点对比
| 优点 | 缺点 | |
|---|---|---|
| 邻接矩阵 | 实现简单,能同时求任意顶点的出度和入度 | 在存储稀疏图时会造成空间浪费 |
| 邻接表 | 使用数组链表实现,不会造成空间浪费 | 不能同时求出任意顶点的出度和入度, 除非同时构建邻接表和逆邻接表,对边 进行操作时需要操作两次 |
| 十字链表 | 使用数组链表实现,不会造成空间浪费 同时可以求出某个顶点的入度和出度 | 对边进行操作时需要操作两次 |
| 邻接多重表 | 对边的操作进行了优化,操作边的次数由两次 减少到了一次 | 删除操作较为复杂 |
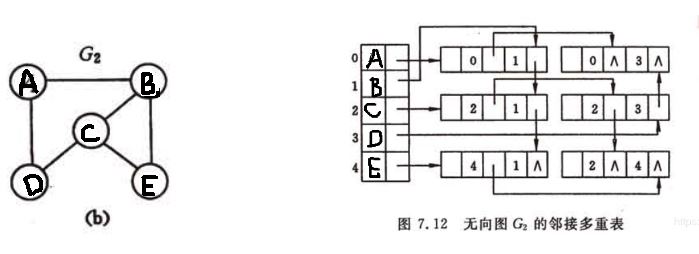
邻接多重表,是在邻接表的基础上改进的,因为十字链表是适合有向图的,所以需要一个数据结构适合无向图,也就是邻接多重表。
对于无向图的邻接表,我们更加关注的重点是顶点,那么是不错的选择,但是我们要是关注的是边的操作。
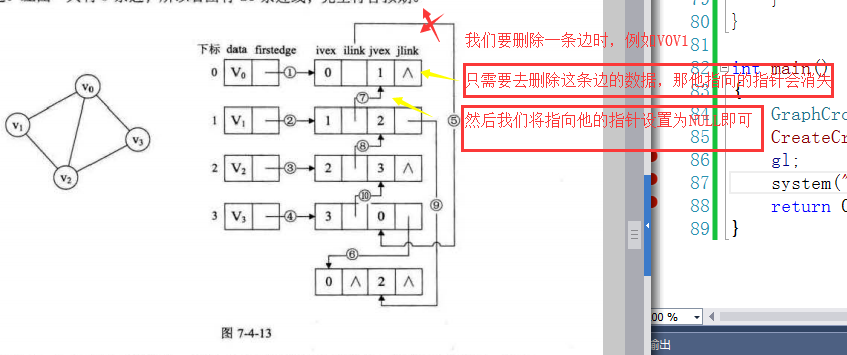
比如:删除一条边,那么我们的操作将变得复杂,我们需要找到这条边的两个顶点,方便去其链表中删除所表示的边。稍微有点麻烦。
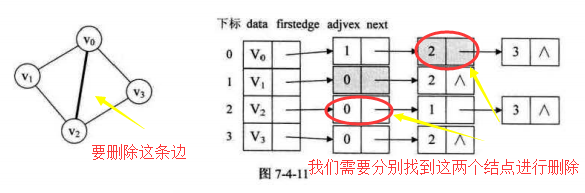
改进
我们只出现无向图中对应条数的边表结点,其他的结构,我们全部由指针来联系,所以当我们想要删除一条边时,就只需要删除对应的边表结点。指向她的指针会置为空,他自己产生的指针会消失。就完成了对边的操作。
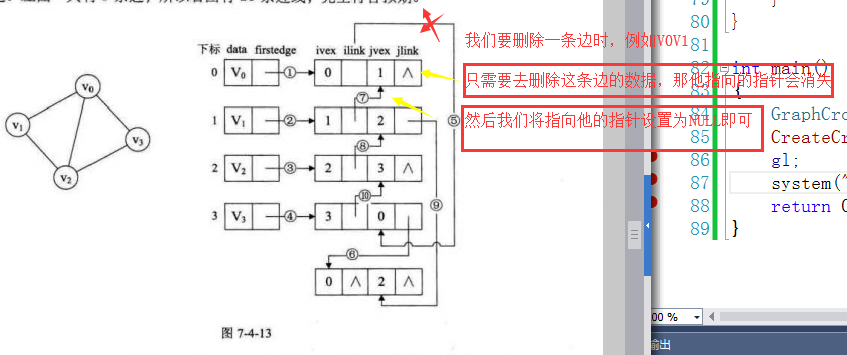
例如上图,我们若是使用邻接表:是要10个顶点结点去表示5条边,而我们若是使用邻接多重表,只需要5个边结点即可。删除一条边就不存在重复操作。
邻接多重表结构
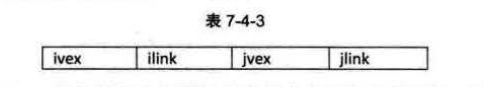
其中ivex和jvex是指某条边依附的两个顶点在顶点表中的下标。ilink指向依附顶点ivex的下一条边,jlink指向依附顶点jvex的下一条边。
再认识下邻接多重表
1.表头结点即顶点结点,与邻接表一样是顺序存储。2.对于每个顶点结点之后是与之相关联的边结点(与该顶点结点相连的边),而邻接表则是一些与顶点结点相连接的点。3.从每个顶点结点开始有一条链表,这条链表将所有与该顶点相连的边都连接了起来。4.邻接多重表中边结点的个数就是无向图中边的数量,又因为无向图中的边必然连接两个顶点,所以便边结点结构中的ilink和jlink会连接两个不同的链表。
java实现
/*** Created by yanfeng-mac on 2017/12/9.* 无向图的邻接多重表的实现* 优点: 使用邻接表在对边进行操作时(如删除),需要两次操作,因为一条边在两个链表里面存储,* 而邻接多重表的优点就在于对边操作时只需要一次操作,这就意味着边只存储一次*/public class GraphMutiplyTable {/*** vName-->顶点名称* firstEdge-->顶点边链表的头结点*/private static class Vertex {private String vName;private Edge firstEdge;public Vertex() {}public Vertex(String name) {this.vName = name;}}/*** iVex-->边的其中一个顶点A* iLink-->边中顶点A的边链表的指针* jVex-->边的另一个顶点B* jLink-->边中顶点B的边链表的指针*/private static class Edge {private int iVex;private Edge iLink;private int jVex;private Edge jLink;public Edge() {}public Edge(int iVex,int jVex) {this.iVex = iVex;this.jVex = jVex;}}private static class GraphEdge {private String vex;private String otherVex;public GraphEdge(String vexName,String otherVexName) {this.vex = vexName;this.otherVex = otherVexName;}}private List<Vertex> vertexArr;public void init(String[] vexArr,List<GraphEdge> edgeList) {initVexArr(vexArr);initEdge(edgeList);}private void initVexArr(String[] vexArr) {vertexArr = new ArrayList<Vertex>(vexArr.length);for(int i = 0;i < vexArr.length;i++) {Vertex vertex = new Vertex(vexArr[i]);vertexArr.add(vertex);}}private void initEdge(List<GraphEdge> edgeList) {for(int i = 0;i < edgeList.size();i++) {GraphEdge graphEdge = edgeList.get(i);if(contains(graphEdge.vex) && contains(graphEdge.otherVex)) {//获取顶点的下标int vIndex = getVexIndex(graphEdge.vex);int oIndex = getVexIndex(graphEdge.otherVex);//获取顶点Vertex vertex = vertexArr.get(vIndex);Vertex oVertex = vertexArr.get(oIndex);//构造两个顶点的边Edge edge = new Edge(vIndex,oIndex);//头插法插入vertex的边//这里一定是从iLink出发,因为ivex相同if(vertex.firstEdge == null) {vertex.firstEdge = edge;} else {Edge vexNextEdge = vertex.firstEdge;edge.iLink = vexNextEdge;vertex.firstEdge = edge;}//头插法插入oVertex的边//这里一定是从jLink出发因为jvex相同if(oVertex.firstEdge == null) {oVertex.firstEdge = edge;} else {Edge oVexNextEdge = oVertex.firstEdge;edge.jLink = oVexNextEdge;oVertex.firstEdge = edge;}}}}private boolean contains(String vName) {for(Vertex vertex : vertexArr) {if(vertex.vName.equals(vName))return true;}return false;}private int getVexIndex(String vName) {for(int i = 0;i < vertexArr.size();i++) {if(vertexArr.get(i).vName.equals(vName))return i;}return -1;}public void print() {for(Vertex vertex : vertexArr) {System.out.println("顶点 " + vertex.vName + " 的所有边: ");int vIndex = getVexIndex(vertex.vName);Edge cursor = vertex.firstEdge;while (cursor != null) {System.out.print(cursor.iVex + "---" + cursor.jVex + " ||");if(cursor.iVex == vIndex) {cursor = cursor.iLink;} else {cursor = cursor.jLink;}}System.out.println();}}//删除边/*** 删除边的整体思路* 1.找到边上的两个顶点A和B* 2.分别遍历AB的边链表,直到找到要删除的边S* 3.分别将边S及边S的前驱边PS的数据存储起来,这里A的要删除的边为cursor,前驱边为preCursor,B的要删除的边为oCursor,前驱边为oPreCursor* 4.调整链表结构* @param graphEdge*/public void remove(GraphEdge graphEdge) {String vName = graphEdge.vex;String oName = graphEdge.otherVex;int vIndex = getVexIndex(vName);int oIndex = getVexIndex(oName);//处理边的第一个顶点AVertex vertex = vertexArr.get(vIndex);Edge cursor = vertex.firstEdge;//指针的前驱Edge preCursor = null;while (cursor != null) {if(cursor.iVex == oIndex || cursor.jVex == oIndex) {//通过遍历顶点A的所有边,找到边的前驱指针break;}preCursor = cursor;if(cursor.iVex == vIndex) {cursor = cursor.iLink;} else {cursor = cursor.jLink;}}//处理边的第二个顶点BVertex oVertex = vertexArr.get(oIndex);Edge oCursor = oVertex.firstEdge;//指针的前驱Edge oPreCursor = null;while (oCursor != null) {if(oCursor.iVex == vIndex || oCursor.jVex == vIndex) {//通过遍历顶点B的所有边,找到边的前驱指针break;}oPreCursor = oCursor;if(oCursor.iVex == oIndex) {oCursor = oCursor.iLink;} else {oCursor = oCursor.jLink;}}if(preCursor != null) {if(preCursor.iVex == vIndex && cursor.iVex == vIndex) {preCursor.iLink = cursor.iLink;} else if(preCursor.iVex == vIndex && cursor.jVex == vIndex) {preCursor.iLink = cursor.jLink;} else if(preCursor.jVex == oIndex && cursor.iVex == vIndex) {preCursor.jLink = cursor.iLink;} else {preCursor.jLink = cursor.jLink;}} else {if(cursor.iVex == vIndex) {vertex.firstEdge = cursor.iLink;} else {vertex.firstEdge = cursor.jLink;}}if(oPreCursor != null) {if(oPreCursor.iVex == oIndex && oCursor.iVex == oIndex) {oPreCursor.iLink = oCursor.iLink;} else if(oPreCursor.iVex == oIndex && oCursor.jVex == oIndex) {oPreCursor.iLink = oCursor.jLink;} else if(oPreCursor.jVex == oIndex && oCursor.iVex == oIndex) {oPreCursor.jLink = oCursor.iLink;} else {oPreCursor.jLink = oCursor.jLink;}} else {if(oCursor.iVex == oIndex) {oVertex.firstEdge = oCursor.iLink;} else {oVertex.firstEdge = oCursor.jLink;}}}public static void main(String[] args) {GraphMutiplyTable graph = new GraphMutiplyTable();String[] vexArr = {"V0","V1","V2","V3"};GraphEdge edge = new GraphEdge("V0","V1");GraphEdge edge1 = new GraphEdge("V0","V2");GraphEdge edge2 = new GraphEdge("V0","V3");GraphEdge edge3 = new GraphEdge("V1","V2");GraphEdge edge4 = new GraphEdge("V2","V3");List<GraphEdge> edgeList = new ArrayList<GraphEdge>();edgeList.add(edge);edgeList.add(edge1);edgeList.add(edge2);edgeList.add(edge3);edgeList.add(edge4);graph.init(vexArr,edgeList);graph.remove(edge3);graph.print();}}